Energy Efficient Light Bulb Options That Will Save You Money

Did you know that you could be saving hundreds of dollars annually on your electricity bill simply by replacing your light bulbs? Gone are the days of light bulbs being mere methods of illuminating your home—today they’re no-brainer energy-saving opportunities for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprints and their monthly utility bills. Outside of traditional incandescent bulbs, there is a wide variety of energy-saving light bulbs that effectively serve the same purpose while delivering more eco-friendly benefits.
If you’re interested in joining homeowners who have already made eco-conscious home upgrades, the easiest place to start is with your lighting. Using this guide, we’ll walk you through the energy-efficient light bulb types you should know about, the specifications and advantages of each, and several other considerations to keep in mind.
Energy-saving light bulb types
Light bulbs have come an astonishingly long way since Thomas Edison’s first 19th-century bulb debuted. Two centuries later, the modern light bulb comes in an expansive assortment of efficiencies, lighting qualities, shapes, and densities.
When it comes to energy-saving light bulbs, the options narrow to three dominant types: halogen incandescent, compact fluorescent lamps, and light-emitting diodes.
1. Halogen Incandescent
For those looking for a light bulb that offers increased efficiency but maintains the same visual appeal of a traditional incandescent light bulb, a halogen incandescent bulb merges the best of both worlds. Though incredibly similar to traditional bulbs, halogen bulbs contain bromine rather than nitrogen-argon, which means the two operate and produce light differently.
Though they may not be the most popular energy-efficient light bulbs for household use, halogen incandescent light bulbs are well-lauded for their high efficiency, bright light quality, and durability. Because they so closely mimic the visual appeal and performance of traditional incandescent light bulbs, making the switch from traditional bulbs is seamless when you opt for halogen incandescent bulbs.
In addition to being the perfect substitute for traditional light bulbs, halogen incandescent light bulbs use about 25% less energy.
Pros:
-
Carry the same look and feel of traditional incandescent bulbs
-
Instantly produce full illumination capacity
-
Cast a relaxing yellow tone rather than an awakening blue tone
-
Produce the same amount of light as a traditional incandescent bulb while using 25% less energy
-
Safe to dispose of bulbs in with regular trash
Cons:
-
Slightly more expensive than traditional incandescent bulbs
-
Generate high heat levels
-
Touching the bulb can reduce its lifespan
2. Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs)
Best recognized by their iconic spiral shape, CFL bulbs were born out of a need for more energy-efficient light bulbs. Home to many small working parts, CFL bulbs emit light from a variety of phosphors inside the bulb and use the same technology as conventional fluorescent bulbs on a far more compact scale.
Typically engineered to last about 10,000 hours and use a fraction of the energy required to power traditional incandescent bulbs, energy-saving CFL bulbs are far more cost-effective than their more popular sibling. Though you’ll pay a higher upfront cost per bulb, recouping the costs typically takes only nine months.
Notably, CFLs do not brighten as quickly as incandescent or halogen bulbs, so they aren’t excellent options for spaces where you will need immediate, bright light. CFL bulbs are also not the best choice for cold climates or outdoor settings, so it’s best to power your indoor lamps with this type of light bulb. CFLs aren't great choices for entryways or places where you need immediate light.
A significant downside is that CFL bulbs contain small amounts of mercury, which can make appropriate disposal difficult. If you’re looking to make eco-conscious choices, be prepared to take the extra step necessary to ensure the toxic chemicals inside CFLs stay out of landfills.
Pros:
-
Require less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs
-
Generate an evenly-spread bright illumination
-
Available in a variety of soft, warm, and bright white hues
-
Cost-effective for their energy-efficient specs
Cons:
-
Sensitive to cold temperatures and colder climates
-
Do not offer immediate, full-brightness
-
Contain toxic mercury
-
Cannot be used with a dimmer switch
3. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
As the most popular type of energy-efficient light bulbs, LED lights are the most flexible lighting option in the modern market. Offering higher efficiency than incandescent and CFL bulbs, LED light bulbs emit light that renders a brilliance incredibly similar to natural daylight.
LED light bulbs use even less energy than CFLs and last up to 50,000 hours, which is a jaw-dropping 40,000 additional hours. Unlike CFLs, LED bulbs reach their full brightness when switched on, so you will never have to wait for illumination. Using LEDs can help you save up to 80% in energy costs per year. While they also come at a heftier cost than CFLs or halogen bulbs, the benefits of an extremely long lifespan means that LEDs can last for years needing to be replaced.
LED bulbs are easy to find in your local hardware store and are available in a wide variety of wattages, shapes, and colors. There’s no need to worry about excessive heat generation; LEDs produce very low levels of heat as compared to CFLs and halogen incandescents.
Pros:
-
Instant full-brightness when powered on
-
Stay cool to the touch even after use
-
Offer lifespans up to five times longer than CFLs
-
No sensitivity to cold climates or temperatures
-
Great for directional light and spotlights
-
Available in soft, warm, and bright white hues
Cons:
-
Dim in brightness over time
-
Not always compatible with dimmers
-
Contain blue light
-
Most expensive light bulb option (but prices continue to trend downward year after year)
CFL vs. LED: Which energy-saving light bulb is better?

While CFL bulbs and LED bulbs were both made as energy-efficient lighting alternatives to traditional incandescent light bulbs, LED bulbs are the newcomer stand out.
CFL bulbs were originally developed to take the place of conventional bulbs and provide a more energy-efficient and eco-friendly glow to your home. Using about 25% of the amount of electricity required to power an incandescent bulb, CFLs also offer a lifespan up to 15 times longer than conventional bulbs.
Though LEDs were not created to replace CFLs, LEDs do offer a range of benefits that ultimately make them the favored option for most property owners. Based solely on energy efficiency alone, LEDs reign supreme. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, ENERGY STAR-qualified LEDs use only 20%–25% of the energy and last up to 25 times longer than traditional incandescent bulbs. Regular LEDs use 25%–30% of the energy and last anywhere between 8 to 25 times longer than halogen incandescent bulbs.
Check out the chart below to see how each bulb type measures up:
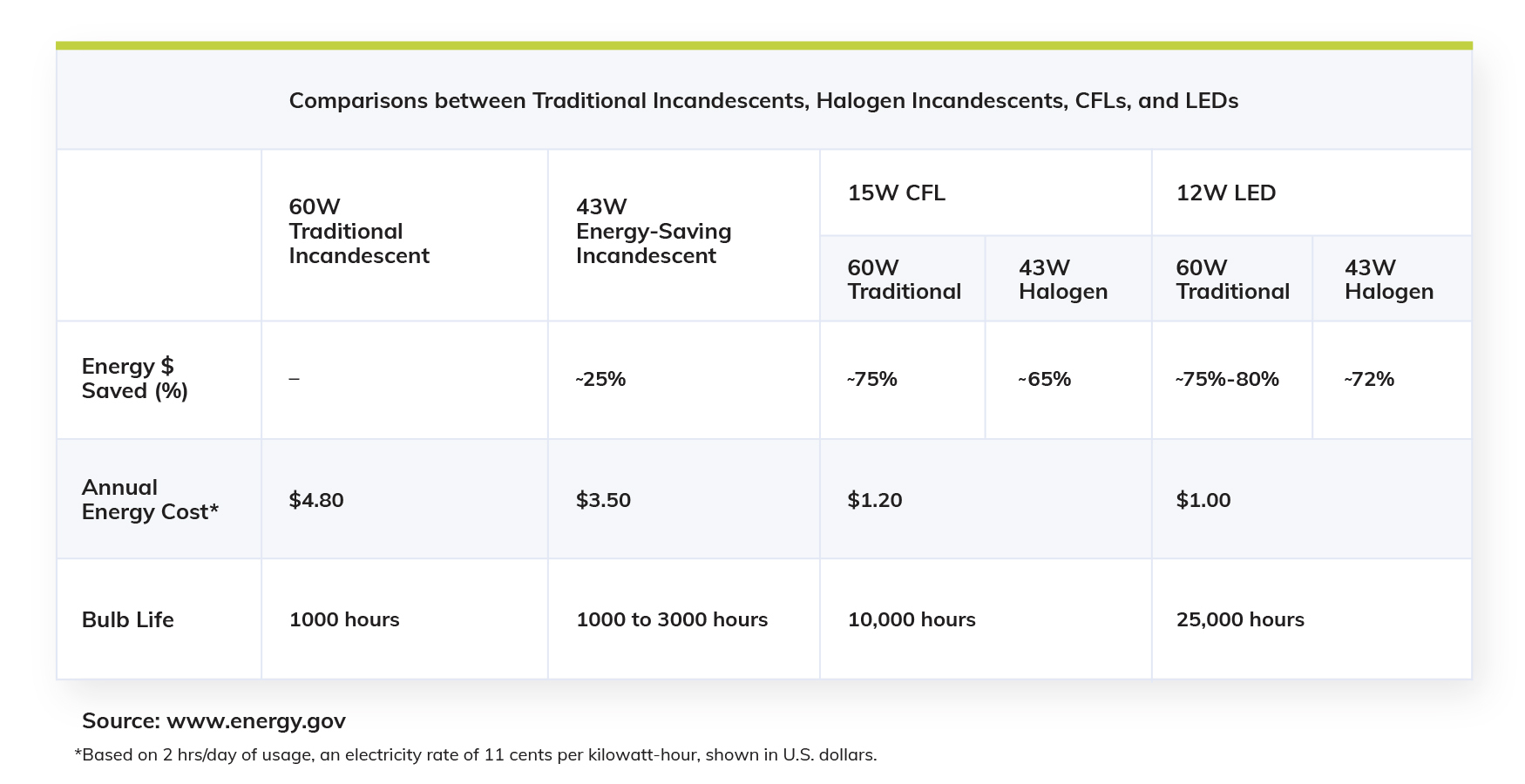
Because LEDs are able to shine brightly indoors and outdoors, in cool climates and warm climates, and offer extremely long lifespans, LEDs tend to be the better bulb choice.
What does an ENERGY STAR certification mean?
Products that have earned an ENERGY STAR certification means they have successfully met the rigid energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. When shopping for energy-saving light bulbs, be on the lookout for products with the iconic blue sticker. And, when you buy ENERGY-STAR labeled light bulbs, you may be eligible for a number of special offers and rebates in addition to annual utility bill savings. There are a number of outstanding benefits to shopping for ENERGY-STAR rated official products.
How much can you save by switching to energy-efficient light bulbs?
While it may seem that making changes as minimal as a light bulb may have little to no reward, making the swap can actually save you a valuable chunk of money, month over month, and year after year. According to a study completed by the U.S. Department of Energy, switching out your home's five most frequently used light fixtures or bulbs with energy-efficient models can save you an average of $75 each year.
Among the many alternative energy upgrades to consider making, updating your lighting with energy-efficient light bulbs is among the easiest and most cost-effective.




